IBD in Children and Adolescents
IBD in Children and Adolescents
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic condition that affects the digestive system, causing persistent inflammation in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. While IBD is often associated with adults, it is increasingly being diagnosed in children and adolescents. Early detection and timely management are crucial, as IBD can significantly impact a child’s growth, nutrition, and overall quality of life.
Dr. Harshad V. Joshi, an experienced Gastroenterologist in Mumbai, specializes in diagnosing and managing IBD in children and adolescents. With compassionate care and advanced treatment strategies, he helps young patients and their families navigate this challenging condition effectively.
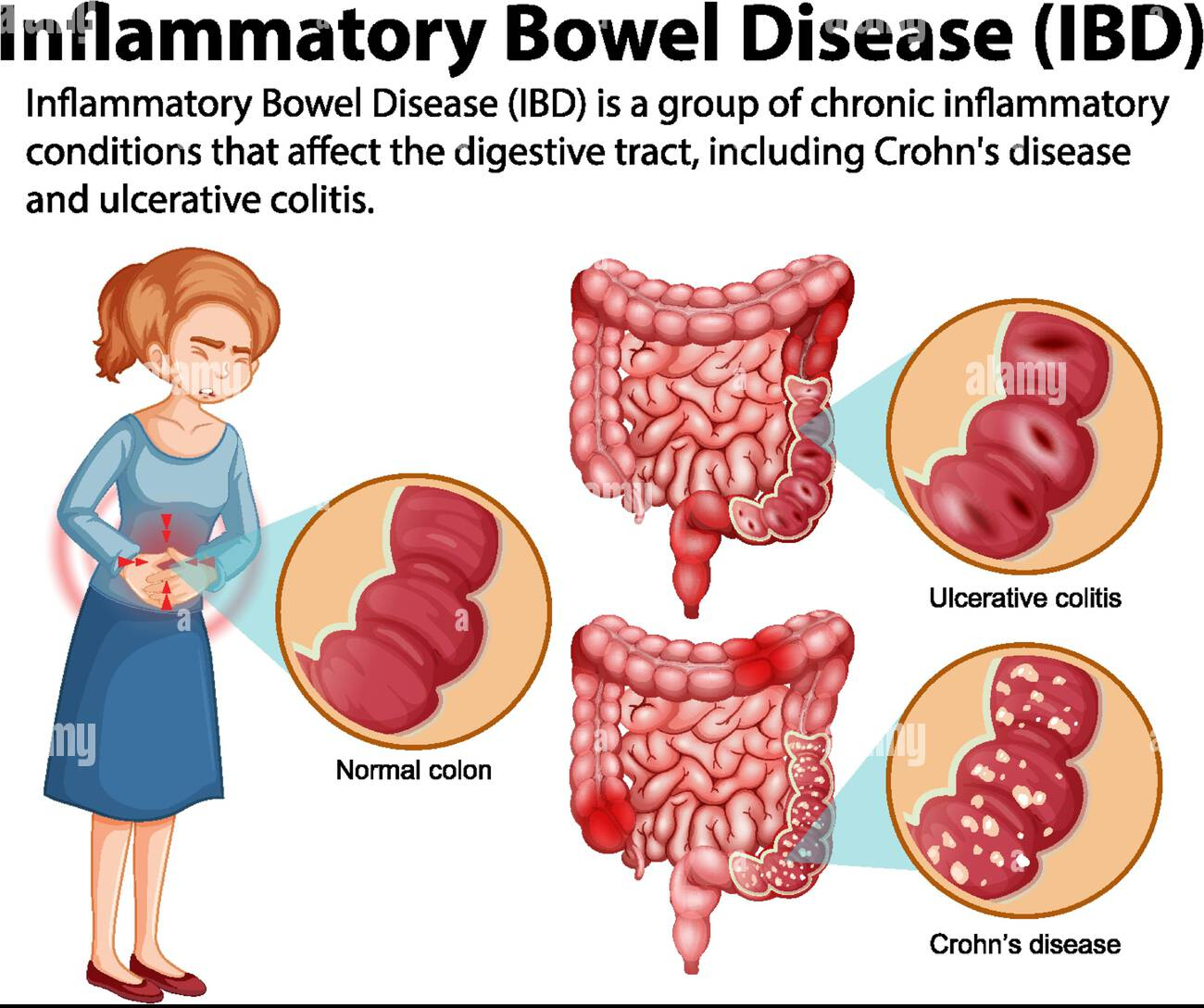
Types of IBD in Children
Two major types of IBD can occur in children and teenagers:
- Crohn’s Disease
- Affects any part of the GI tract from mouth to anus.
- Inflammation can spread deep into the intestinal walls.
- Symptoms may include abdominal pain, chronic diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue.
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Primarily affects the colon and rectum.
- Inflammation is limited to the innermost lining of the large intestine.
- Symptoms include bloody stools, abdominal cramping, and urgency to pass stools.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of IBD is not fully understood, but several factors contribute:
- Genetics: Family history increases the risk.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Abnormal immune response against the intestines.
- Environmental Factors: Diet, pollution, and infections may trigger symptoms.
- Lifestyle: Stress and poor nutrition can worsen the condition.
Symptoms of IBD in Children and Adolescents
Children and teenagers with IBD may present with a variety of symptoms that can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions. Common signs include:
- Persistent abdominal pain and cramps
- Chronic diarrhea, sometimes with blood or mucus
- Weight loss and poor appetite
- Fatigue and low energy
- Delayed growth or puberty
- Frequent urgency to use the bathroom
Early diagnosis is important to prevent complications such as malnutrition, intestinal damage, and emotional stress.
Diagnosis of IBD
Dr. Harshad Joshi uses advanced diagnostic tools to identify IBD in young patients. These may include:
- Blood tests to check for anemia and inflammation
- Stool tests to rule out infections and detect inflammation markers
- Endoscopy or colonoscopy to directly view the digestive tract
- Imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to assess the extent of disease
Treatment Options
Treatment of IBD in children focuses on controlling inflammation, reducing symptoms, promoting growth, and improving quality of life. Dr. Joshi offers a personalized treatment approach that may include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, and biologic therapies.
- Nutritional Support: Special diets and supplements to correct deficiencies and support growth.
- Lifestyle Guidance: Stress management, healthy eating, and regular exercise.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be needed to remove damaged portions of the intestine.
Living with IBD as a Child or Teen
IBD can be overwhelming for children and their families. Emotional support, regular follow-ups, and open communication with a specialist are essential. With the right medical care, most children with IBD can manage their condition effectively and lead healthy, active lives.
At Dr. Harshad Joshi’s clinic in Mumbai, parents and children receive not only medical treatment but also education, guidance, and emotional support to cope with IBD.
Book Your Session Today
If your child is experiencing symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, or growth concerns, it is important to seek professional care at the earliest. Dr. Harshad V. Joshi, an expert Gastroenterologist in Mumbai, provides compassionate and specialized treatment for IBD in children and adolescents.
Book an AppointmentFrequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No, IBD is a chronic condition that requires lifelong management. However, with proper treatment, symptoms can be well controlled.
No, IBD is an inflammatory disease that damages the intestine, whereas IBS is a functional disorder without inflammation.
Most children manage IBD with medications, but surgery may be needed if the disease is severe or complications occur.
Diet plays a major role in managing symptoms and improving nutrition, but it cannot cure IBD. Medical treatment is essential.
Regular follow-ups are recommended to monitor growth, nutrition, and disease activity. The frequency depends on the severity of the condition.
