Foreign Body Removal
Foreign Body Removal
A foreign body (FB) is any object originating outside the body of an organism. In machinery, it can mean any unwanted intruding object. Most references to foreign bodies involve propulsion through natural orifices into hollow organs. Foreign bodies can be inert or irritating. If they irritate they will cause inflammation and scarring. They can bring infection into the body or acquire infectious agents and protect them from the body’s immune defenses. They can obstruct passageways either by their size or by the scarring they cause. Some can be toxic or generate toxic chemicals from reactions with chemicals produced by the body, as is the case with many examples of ingested metal objects.
Foreign Body Removal
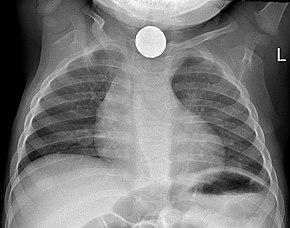
Endoscopic foreign body removal is a medical procedure performed to extract objects or foreign bodies that have become lodged within the body’s internal passages or cavities. Endoscopy involves the use of a flexible tube with a camera and light on its tip, known as an endoscope, to visualize and manipulate the foreign object. This technique is used to avoid the need for invasive surgery, which might otherwise be required to remove the object.

Endoscopic foreign body removal is commonly performed for various situations, such as:
- Throat and Esophageal Foreign Bodies: Objects accidentally swallowed, such as coins, toys, or pieces of food, can become lodged in the throat or esophagus and may require endoscopic removal.
• Nasal Foreign Bodies: Small objects that get stuck in the nose, particularly in children, can be extracted through nasal endoscopy.
• Gastrointestinal Foreign Bodies: Objects that are accidentally ingested and pass into the stomach or intestines may require endoscopic removal if they become trapped or cause discomfort.
The procedure is generally safe and effective, and it helps avoid more invasive surgical interventions. The decision to perform endoscopic foreign body removal is based on the type and location of the foreign body, as well as the patient’s overall health. The procedure is typically carried out by a gastroenterologist, otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat specialist), or other medical professionals trained in endoscopic techniques.

